React Native启动流程
2018-04-28 小文字
背景
本文主要针对 react-native 创建模板工过程中,涉及的一些细节流程和实现原理做分析。
启动流程分析
根据API教程示例,启动一个模板工程在Android模拟器或者真机上,只需要执行
react-native run-android
通过分析启动流程的源代码,我们得出以下流程图:
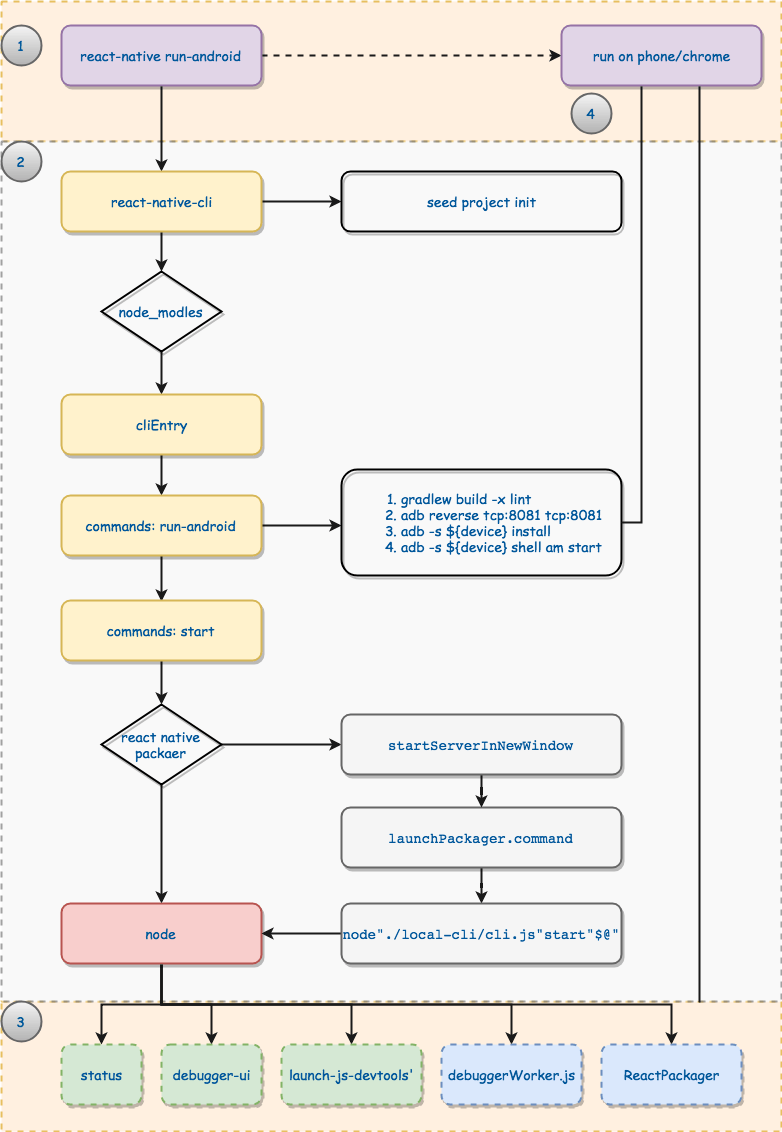
我们就从react-native和他的参数解析开始,首先需要找到react-native的真身。为什么这么说的呢?
react-native 分析
一般来说某一个命令安装到本地后都会配置系统环境变量,然后通过创建一个软引用将命令指向真实的实现,
aven-mac-pro-2:AwesomeProject aven$ which react-native
/usr/local/bin/react-native
aven-mac-pro-2:AwesomeProject aven$ ls -al /usr/local/bin/react-native
lrwxr-xr-x 1 aven admin 45 Jan 16 2016 /usr/local/bin/react-native -> ../lib/node_modules/react-native-cli/index.js
因此我们知道react-native的实际就是:/usr/local/lib/node_modules/react-native-cli/index.js
所以我们知道,react-native这个脚本实际上是一个node程序react-native-cli,入口为index.js
在分析index.js之前,我们先看一下他的文档注释。 大致意思是,react-native-cli是一个安装在全局环境,这一点我们已经知道。因此要做版本升级和重大改动都不是很方便,你不能总是要求开发者频繁升级react-native-cli. 所以react naitve在设计这个脚本工具的时候就考虑了这一点,全局安装的只是一个转发器,直接将参数转发给具体工程的内部实现体。这及解决了react-native升级问题,又解决了不同工程使用不同版本的诉求。
react-native-cli的职责是初始化一个种子工程,然后转发所有命令参数给工程本地的react-native。
#!/usr/bin/env node
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// /!\ DO NOT MODIFY THIS FILE /!\
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
//
// react-native-cli is installed globally on people's computers. This means
// that it is extremely difficult to have them upgrade the version and
// because there's only one global version installed, it is very prone to
// breaking changes.
//
// The only job of react-native-cli is to init the repository and then
// forward all the commands to the local version of react-native.
//
// If you need to add a new command, please add it to local-cli/.
//
// The only reason to modify this file is to add more warnings and
// troubleshooting information for the `react-native init` command.
//
// Do not make breaking changes! We absolutely don't want to have to
// tell people to update their global version of react-native-cli.
//
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// /!\ DO NOT MODIFY THIS FILE /!\
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
那么转发的目标具体是谁呢,我们可以简单分析下index.js来获取答案。
react-native-cli 分析
经过分析我们可以总结出一下几个关键点:
| # | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 检查版本参数 -v或者–version |
| 2 | react-native存在,执行run方法 |
| 3 | react-native不存在,执行react-native-cli |
| 4 | init创建种子工程 |
| 5 | 初始化种子工程 |
- 检查版本参数
-v或者--version
如果执行react-native的时候输入了参数-v或者--version,那么输出react-native-cli和本地react-native的版本号,实现代码如下:
function checkForVersionArgument() {
if (process.argv.indexOf('-v') >= 0 || process.argv.indexOf('--version') >= 0) {
console.log('react-native-cli: ' + require('./package.json').version);
try {
console.log('react-native: ' + require(REACT_NATIVE_PACKAGE_JSON_PATH()).version);
} catch (e) {
console.log('react-native: n/a - not inside a React Native project directory')
}
process.exit();
}
}
这个我们可以试一下:
aven-mac-pro-2:AwesomeProject aven$ react-native -v
react-native-cli: 0.1.10
react-native: 0.55.3
- react-native存在,执行run方法
接着会检查当前目录下(当前工程)有没有一个本地的react-native版本,有的话,执行他的run方法:
var CLI_MODULE_PATH = function() {
return path.resolve(
process.cwd(),
'node_modules',
'react-native',
'cli.js'
);
};
var cli;
var cliPath = CLI_MODULE_PATH();
if (fs.existsSync(cliPath)) {
cli = require(cliPath);
}
if (cli) {
cli.run();
}
- react-native不存在,执行react-native-cli
如果react-native不存在,那么尝试由react-native-cli自身来处理。怎么处理呢?前面说过了,他只支持初始化一个种子工程,比如:react-native init。
所以下面的代码也就比较好理解了。
- 首先确认参数个数,
- 第一个参数必须为init,其他都不支持
- 第二个参数是项目名,可选的支持verbose日志输出
- 没有参数,或者第一个参数不是init,没有第二个参数都是不合法的情况,输出错误提示
var args = process.argv.slice(2);
if (args.length === 0) {
console.error(
'You did not pass any commands, did you mean to run `react-native init`?'
);
process.exit(1);
}
switch (args[0]) {
case 'init':
if (args[1]) {
var verbose = process.argv.indexOf('--verbose') >= 0;
init(args[1], verbose);
} else {
console.error(
'Usage: react-native init <ProjectName> [--verbose]'
);
process.exit(1);
}
break;
default:
console.error(
'Command `%s` unrecognized. ' +
'Did you mean to run this inside a react-native project?',
args[0]
);
process.exit(1);
break;
}
- init创建种子工程
初始化种子工程时,会校验一下工程目录的名字,需要满足命名规则,具体为一个正则表达式:/^[$A-Z_][0-9A-Z_$]*$/i
必须是大小写字母,或者下划线开头,数字,大小写字母,下划线结尾
除了命名规则,也需要确认下当前名字是不是已经在本地存在,存在则给予选择提示,否则继续创建
function init(name, verbose) {
validatePackageName(name);
if (fs.existsSync(name)) {
createAfterConfirmation(name, verbose);
} else {
createProject(name, verbose);
}
}
创建模板工程,包括目录创建,和package.json创建,已经react-native的安装。
npm install --save react-native
- 初始化种子工程
最后执行本地react-native的初始化init方法
cli = require(CLI_MODULE_PATH());
cli.init(root, projectName);
本地react-native
现在我们看下参数转发到本地react-native后,是怎么处理的:<project-dir>/node_modles/react-native/cli.js
查看代码我们知道cli.js实际上只是一个暴露的出口,具体逻辑还是从./local-cli/cli.js来, 调用cliEntry的run方法。
'use strict';
// gracefulify() has to be called before anything else runs
require('graceful-fs').gracefulify(require('fs'));
// This file must be able to run in node 0.12 without babel so we can show that
// it is not supported. This is why the rest of the cli code is in `cliEntry.js`.
require('./server/checkNodeVersion')();
require('../setupBabel')();
var cliEntry = require('./cliEntry');
if (require.main === module) {
cliEntry.run();
}
module.exports = cliEntry;
function run() {
const setupEnvScript = /^win/.test(process.platform)
? 'setup_env.bat'
: 'setup_env.sh';
childProcess.execFileSync(path.join(__dirname, setupEnvScript));
commands.forEach(cmd => addCommand(cmd, config));
commander.parse(process.argv);
const isValidCommand = commands.find(cmd => cmd.name.split(' ')[0] === process.argv[2]);
if (!isValidCommand) {
printUnknownCommand(process.argv[2]);
return;
}
if (!commander.args.length) {
commander.help();
}
}
commands汇总了所有支持的命令参数,包括三部分:
const commands: Array<CommandT> = [
...documentedCommands,
...undocumentedCommands,
...getProjectCommands(),
];
本文我们关注的run-android在documentedCommands部分。
const documentedCommands = [
require('./server/server'),
require('./runIOS/runIOS'),
require('./runAndroid/runAndroid'),
require('./library/library'),
require('./bundle/bundle'),
require('./bundle/unbundle'),
require('./eject/eject'),
require('./link/link'),
require('./link/unlink'),
require('./install/install'),
require('./install/uninstall'),
require('./upgrade/upgrade'),
require('./logAndroid/logAndroid'),
require('./logIOS/logIOS'),
require('./dependencies/dependencies'),
require('./info/info'),
];
具体实现逻辑参考:<project-dir>/node_modles/react-native/local-cli/runAndroid/runAndroid.js
run-android流程
现在我们分析run-android具体做的事情。
在执行了react-native run-android之后,我们可以看到,终端被重新开启了一个,两个终端分别在运行。
run-android的定义如下:
module.exports = {
name: 'run-android',
description: 'builds your app and starts it on a connected Android emulator or device',
func: runAndroid,
options: [{
command: '--install-debug',
}, {
command: '--root [string]',
description: 'Override the root directory for the android build (which contains the android directory)',
default: '',
}, {
command: '--flavor [string]',
description: '--flavor has been deprecated. Use --variant instead',
}, {
command: '--variant [string]',
}, {
command: '--appFolder [string]',
description: 'Specify a different application folder name for the android source.',
default: 'app',
}, {
command: '--appId [string]',
description: 'Specify an applicationId to launch after build.',
default: '',
}, {
command: '--appIdSuffix [string]',
description: 'Specify an applicationIdSuffix to launch after build.',
default: '',
}, {
command: '--main-activity [string]',
description: 'Name of the activity to start',
default: 'MainActivity',
}, {
command: '--deviceId [string]',
description: 'builds your app and starts it on a specific device/simulator with the ' +
'given device id (listed by running "adb devices" on the command line).',
}, {
command: '--no-packager',
description: 'Do not launch packager while building',
}, {
command: '--port [number]',
default: process.env.RCT_METRO_PORT || 8081,
parse: (val: string) => Number(val),
}],
};
命中run-android命令后执行方法runAndroid:
/**
* Starts the app on a connected Android emulator or device.
*/
function runAndroid(argv, config, args) {
if (!checkAndroid(args.root)) {
const reactNativeScriptsPath = findReactNativeScripts();
if (reactNativeScriptsPath) {
child_process.spawnSync(
reactNativeScriptsPath,
['android'].concat(process.argv.slice(1)),
{stdio: 'inherit'}
);
} else {
console.log(chalk.red('Android project not found. Maybe run react-native android first?'));
}
return;
}
if (!args.packager) {
return buildAndRun(args);
}
return isPackagerRunning(args.port).then(result => {
if (result === 'running') {
console.log(chalk.bold('JS server already running.'));
} else if (result === 'unrecognized') {
console.warn(chalk.yellow('JS server not recognized, continuing with build...'));
} else {
// result == 'not_running'
console.log(chalk.bold('Starting JS server...'));
startServerInNewWindow(args.port);
}
return buildAndRun(args);
});
}
多次执行,并不会重复启动打包服务多次,因为每次run的时候,都会检测打包服务是否正在运行,检测方法为,发送一个GET请求,根据返回值来判断, 端口号默认是是8081,也可以指定:
/**
* Indicates whether or not the packager is running. It returns a promise that
* when fulfilled can returns one out of these possible values:
* - `running`: the packager is running
* - `not_running`: the packager nor any process is running on the expected
* port.
* - `unrecognized`: one other process is running on the port we expect the
* packager to be running.
*/
function isPackagerRunning(packagerPort = (process.env.RCT_METRO_PORT || 8081)) {
return fetch(`http://localhost:${packagerPort}/status`).then(
res => res.text().then(body =>
body === 'packager-status:running' ? 'running' : 'unrecognized'
),
() => 'not_running'
);
}
启动一个新的进程,并打开一个termianl的具体实现如下:
function startServerInNewWindow(port) {
const scriptFile = /^win/.test(process.platform) ?
'launchPackager.bat' :
'launchPackager.command';
const scriptsDir = path.resolve(__dirname, '..', '..', 'scripts');
const launchPackagerScript = path.resolve(scriptsDir, scriptFile);
const procConfig = {cwd: scriptsDir};
const terminal = process.env.REACT_TERMINAL;
// setup the .packager.env file to ensure the packager starts on the right port
const packagerEnvFile = path.join(__dirname, '..', '..', 'scripts', '.packager.env');
const content = `export RCT_METRO_PORT=${port}`;
// ensure we overwrite file by passing the 'w' flag
fs.writeFileSync(packagerEnvFile, content, {encoding: 'utf8', flag: 'w'});
if (process.platform === 'darwin') {
if (terminal) {
return child_process.spawnSync('open', ['-a', terminal, launchPackagerScript], procConfig);
}
return child_process.spawnSync('open', [launchPackagerScript], procConfig);
} else if (process.platform === 'linux') {
procConfig.detached = true;
if (terminal){
return child_process.spawn(terminal, ['-e', 'sh ' + launchPackagerScript], procConfig);
}
return child_process.spawn('sh', [launchPackagerScript], procConfig);
} else if (/^win/.test(process.platform)) {
procConfig.detached = true;
procConfig.stdio = 'ignore';
return child_process.spawn('cmd.exe', ['/C', launchPackagerScript], procConfig);
} else {
console.log(chalk.red(`Cannot start the packager. Unknown platform ${process.platform}`));
}
}
分析代码我们可以知道,打开一个终端,在mac下用的是open命令,这个命令可以打开文件,或者指定打开的程序,这里是指定程序,参数为-a
aven-mac-pro-2:~ aven$ open -h
Usage: open [-e] [-t] [-f] [-W] [-R] [-n] [-g] [-h] [-s <partial SDK name>][-b <bundle identifier>] [-a <application>] [filenames] [--args arguments]
Help: Open opens files from a shell.
By default, opens each file using the default application for that file.
If the file is in the form of a URL, the file will be opened as a URL.
Options:
-a Opens with the specified application.
-b Opens with the specified application bundle identifier.
-e Opens with TextEdit.
-t Opens with default text editor.
-f Reads input from standard input and opens with TextEdit.
-F --fresh Launches the app fresh, that is, without restoring windows. Saved persistent state is lost, excluding Untitled documents.
-R, --reveal Selects in the Finder instead of opening.
-W, --wait-apps Blocks until the used applications are closed (even if they were already running).
--args All remaining arguments are passed in argv to the application's main() function instead of opened.
-n, --new Open a new instance of the application even if one is already running.
-j, --hide Launches the app hidden.
-g, --background Does not bring the application to the foreground.
-h, --header Searches header file locations for headers matching the given filenames, and opens them.
-s For -h, the SDK to use; if supplied, only SDKs whose names contain the argument value are searched.
Otherwise the highest versioned SDK in each platform is used.
新窗口执行的具体内容实际上就是开始一个node程序,入口为cli.js
node "./local-cli/cli.js" start "$@"
这就尴尬了,我们前面分析入口的时候run-android就是一步步冲cli.js调用的,这里咋看起来有绕回去了,那么实际上是这样的么?
简单回答,是的。并且如果你打开工程的package.json看一下,会发现其中定义的start命令指向相同内容:
{
"name": "AwesomeProject",
"version": "0.0.1",
"private": true,
"scripts": {
"start": "node node_modules/react-native/local-cli/cli.js start",
"test": "jest"
},
"dependencies": {
"react": "16.3.1",
"react-native": "^0.55.3"
},
"devDependencies": {
"babel-jest": "22.4.3",
"babel-preset-react-native": "4.0.0",
"jest": "22.4.3",
"react-test-renderer": "16.3.1"
},
"jest": {
"preset": "react-native"
}
}
那么如何理解呢?
前面执行的时候是react-native run-android最终间接等价于node node_modules/react-native/local-cli/cli.js run-android
看出区别了么?
实际上新开的窗口和老窗口都是执行了cli.js这个node程序,只不过大家参数不同,所以启动打包服务的参数实际上就是start。
所以我们也可以手工执行npm start来启动打包服务。
aven-mac-pro-2:AwesomeProject aven$ npm start
> [email protected] start /Users/aven/projects-react-native/AwesomeProject
> node node_modules/react-native/local-cli/cli.js start
Scanning folders for symlinks in /Users/aven/projects-react-native/AwesomeProject/node_modules (12ms)
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ │
│ Running Metro Bundler on port 8081. │
│ │
│ Keep Metro running while developing on any JS projects. Feel free to │
│ close this tab and run your own Metro instance if you prefer. │
│ │
│ https://github.com/facebook/react-native │
│ │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Looking for JS files in
/Users/aven/projects-react-native/AwesomeProject
Metro Bundler ready.
Loading dependency graph, done.
BUNDLE [android, dev] ./index.js ▓▓▓▓▓▓▓▓▓▓▓▓▓▓▓▓ 100.0% (485/485), done.
这里start的具体实现,我们只需要回到commands的定义去看下,start是在哪里定义的就知道他的具体实现了。
源码位置为:<project-dir>/node_modles/react-native/local-cli/server/server.js
start的定义如下:
module.exports = {
name: 'start',
func: server,
description: 'starts the webserver',
options: [{
command: '--port [number]',
default: process.env.RCT_METRO_PORT || 8081,
parse: (val: string) => Number(val),
}, {
command: '--host [string]',
default: '',
}, {
command: '--root [list]',
description: 'add another root(s) to be used by the packager in this project',
parse: (val: string) => val.split(',').map(root => path.resolve(root)),
default: [],
}, {
command: '--projectRoots [list]',
description: 'override the root(s) to be used by the packager',
parse: (val: string) => val.split(','),
default: (config: ConfigT) => config.getProjectRoots(),
}, {
command: '--assetExts [list]',
description: 'Specify any additional asset extensions to be used by the packager',
parse: (val: string) => val.split(','),
default: (config: ConfigT) => config.getAssetExts(),
}, {
command: '--sourceExts [list]',
description: 'Specify any additional source extensions to be used by the packager',
parse: (val: string) => val.split(','),
default: (config: ConfigT) => config.getSourceExts(),
}, {
command: '--platforms [list]',
description: 'Specify any additional platforms to be used by the packager',
parse: (val: string) => val.split(','),
default: (config: ConfigT) => config.getPlatforms(),
}, {
command: '--providesModuleNodeModules [list]',
description: 'Specify any npm packages that import dependencies with providesModule',
parse: (val: string) => val.split(','),
default: (config: RNConfig) => {
if (typeof config.getProvidesModuleNodeModules === 'function') {
return config.getProvidesModuleNodeModules();
}
return null;
},
}, {
command: '--max-workers [number]',
description: 'Specifies the maximum number of workers the worker-pool ' +
'will spawn for transforming files. This defaults to the number of the ' +
'cores available on your machine.',
parse: (workers: string) => Number(workers),
}, {
command: '--skipflow',
description: 'Disable flow checks'
}, {
command: '--nonPersistent',
description: 'Disable file watcher'
}, {
command: '--transformer [string]',
description: 'Specify a custom transformer to be used'
}, {
command: '--reset-cache, --resetCache',
description: 'Removes cached files',
}, {
command: '--custom-log-reporter-path, --customLogReporterPath [string]',
description: 'Path to a JavaScript file that exports a log reporter as a replacement for TerminalReporter',
}, {
command: '--verbose',
description: 'Enables logging',
}, {
command: '--https',
description: 'Enables https connections to the server',
}, {
command: '--key [path]',
description: 'Path to custom SSL key',
}, {
command: '--cert [path]',
description: 'Path to custom SSL cert',
}],
};
start触发了server方法,启动了react-native的打包服务
/**
* Starts the React Native Packager Server.
*/
function server(argv: mixed, config: RNConfig, allArgs: Object) {
const {root, ...args} = allArgs;
args.projectRoots = args.projectRoots.concat(root);
const startedCallback = logReporter => {
logReporter.update({
type: 'initialize_started',
port: args.port,
projectRoots: args.projectRoots,
});
process.on('uncaughtException', error => {
logReporter.update({
type: 'initialize_failed',
port: args.port,
error,
});
process.exit(11);
});
};
const readyCallback = logReporter => {
logReporter.update({
type: 'initialize_done',
});
};
const runServerArgs: RunServerArgs = args;
/* $FlowFixMe: ConfigT shouldn't be extendable. */
const configT: ConfigT = config;
runServer(runServerArgs, configT, startedCallback, readyCallback);
}
前面分析过,打包服务如果已经在运行中了,是不需要重复启动的,这个是通过HTTP请求一个status的来查询。那么这个status的服务也可以很快查到:
具体是statusPageMiddleware中间件。
const app = connect()
.use(loadRawBodyMiddleware)
.use(compression())
.use(
'/debugger-ui',
serveStatic(path.join(__dirname, 'util', 'debugger-ui')),
)
.use(
getDevToolsMiddleware(args, () => wsProxy && wsProxy.isChromeConnected()),
)
.use(getDevToolsMiddleware(args, () => ms && ms.isChromeConnected()))
.use(openStackFrameInEditorMiddleware(args))
.use(copyToClipBoardMiddleware)
.use(statusPageMiddleware)
.use(systraceProfileMiddleware)
.use(indexPageMiddleware)
.use(packagerServer.processRequest.bind(packagerServer));
/**
* Status page so that anyone who needs to can verify that the packager is
* running on 8081 and not another program / service.
*/
module.exports = function(req, res, next) {
if (req.url === '/status') {
res.end('packager-status:running');
} else {
next();
}
};
运行Andorid工程
现在打包服务已经ok,剩下的就是讲android app运行起来。基本就死执行gradle和adb的命令,没什么好说的:
- gradlew build -x lint
- adb reverse tcp:8081 tcp:8081
- adb -s ${device} install ${args.appFolder}/build/outputs/apk/${args.appFolder}-debug.apk
- adb -s ${device} shell am start -n ${packageNameWithSuffix}/${packageName}.${mainActivity}
小结
分析到这儿,可以发现整个react-native的启动逻辑还是比较多的,主要是一些命令行工作,包括以下几部分:
- 脚本
重定向,react-native(全局),react-native-cli,react-native(本地工程) - 启动打包服务,提供一些接口支持,比如status等,node cli.js start
- 编译apk,gradlew build
- adb reverse
- 安装并启动app,adb install